Contributed by Jody Muelaner
Open cable carriers have an open chain-link structure with cross bars that contain cables and hoses. Enclosed cable carriers form a complete tube; this can be achieved using a chain-link structure with sliding covers, or as a homogeneous fully sealed corrugated tube, such as a flexible conduit. All cable carriers prevent wear, damage and snagging, by guiding and protecting cables and hoses. Closed cable carriers also provide protection against contaminants. If there is a risk that foreign bodies such as metal chips, or corrosive chemicals, could damage cables, then a closed carrier is the best choice. Where contaminants are not expected to cause any issues, open carriers are often a better choice. Open carriers provide easy access for cable replacement, are lighter and also enable visual inspection of cables. Open carriers are also often less costly.
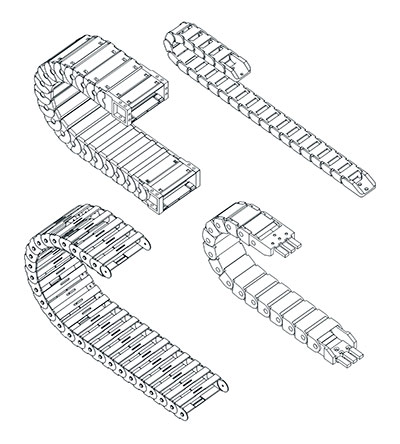 When selecting a closed carrier, the type of contaminant and level or protection will be key considerations. Contaminants can include debris such as metal chips or fluids. Large debris moving at speed may require an enhanced level of mechanical protection, while fluids may be corrosive. Both open and closed cable carriers are available in metal or plastic. While humidity will accelerate corrosion in metal carriers, some chemicals may be more problematic for plastic cable carriers. If there is a requirement to shield cables from very high temperatures then a metal cable carrier may be required.
When selecting a closed carrier, the type of contaminant and level or protection will be key considerations. Contaminants can include debris such as metal chips or fluids. Large debris moving at speed may require an enhanced level of mechanical protection, while fluids may be corrosive. Both open and closed cable carriers are available in metal or plastic. While humidity will accelerate corrosion in metal carriers, some chemicals may be more problematic for plastic cable carriers. If there is a requirement to shield cables from very high temperatures then a metal cable carrier may be required.
Chain-link style enclosed conduits provide the greatest mechanical protection. They have clearly defined limits on bend radius and smooth motion. However, they involve sliding contacts which are difficult to seal completely against small particles and fluids. Corrugated tubes provide a completely sealed cable carrier, but with lower levels of mechanical protection and, especially against heavy forces resulting in a tight bend radius. Another approach to fully enclose cables is to use an open cable carrier with a secondary sliding channel which provides a seal around it. This can be a cost-effective solution, especially for long travels.
Other critical considerations when selecting any cable carrier include the bend radius, sizes and weight of cables, travel distance and axes of motion.







Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.