By Frank Koditek, Product Line Manager, Belden
Since the invention of the stone hammer, tools and equipment have helped humankind achieve great things. Yet, sometimes the equipment can make life a little more challenging too. Take communications cables, for example.

Cables are an important component of the Ethernet-based industrial networks that are becoming more common in industrial facilities. They are installed in facilities that range from factories to power substations to deep-water oil and gas activity to transportation and more. Failure of an industrial network results in expensive downtime, possible loss of product in process, and other undesirable consequences. Cable choices can have a huge impact on system reliability and uptime. Despite the attention paid to the switches and routers that manage the data, the importance of cables is often overlooked.
Cables impact performance, reliability and profitability
It is important to choose the right cable for the job. The majority of industrial network failures occur due to signal transmission issues. Downtime costs for mission critical networks can range from $25,000 per hour for an oil pipeline to $45,000 per hour for a power plant. If damaged or unsuitable cable is at the root of an outage, its duration can be lengthy because it is difficult to troubleshoot cable issues. There is real incentive to identify and install the right product for the job.
No one type of cable fits every need or solves every problem. The first priority in choosing cable for your industrial network application is to understand the importance of specifying industrial grade cable. Yes, it typically costs more, but any such consideration quickly pales the first time the cable fails. Commercial grade cables are designed for commercial settings. They do not have the physical integrity needed to perform consistently in the harsh conditions found in industrial applications.

Industrial cabling is available using copper conductors or fiber optic technology. Copper cabling transmits data through twisted pairs of copper wires and fiber cables transmit data using light. Each has its pros and cons. When deciding which to use in a given application, there are a number of relevant elements to consider.
Cable runs and data transmission rates
Two major differentiators between copper and fiber cabling are the length of the run they are able to sustain and the data volumes they are able to carry.
The length of your cable run will help determine the medium. If your run is 100 m or less, copper cables work well. At greater lengths, fiber has the advantage. Multi-mode fiber cables can run a maximum distance of 2000 m, while single mode fiber cables can maintain signal fidelity over considerably longer distances.
In network communications, bandwidth typically means data transfer rate, i.e. the amount of data that can be transferred from one point to another in a given amount of time. Cat 6 copper cables have a maximum bandwidth of 1 Gb/s, while Cat 5e copper cables top out at 100 Mb/s. These bandwidths are sufficient for most industrial applications today. Nonetheless, when choosing cable, you will want to consider future requirements, as well as plan for the “bandwidth creep” that has been the hallmark of industrial networks. Fiber cables transmit at data rates of 10 Gb/s or more and are recommended for network backbones, security applications with numerous digital cameras attached and other high-bandwidth applications.
Other considerations
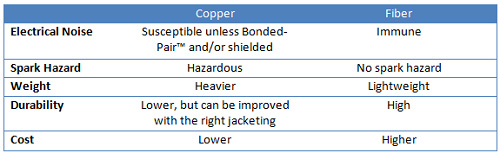
Once you have determined the distances to be supported and the required data rate, there are a variety of other considerations that must be taken into account. Some of those considerations are security, spark hazard, durability and noise immunity.
Security – Many industries are considered potential terrorist targets. Sabotage, espionage and theft are real threats. If your cable runs between buildings or in other less-secure environments, you will want to consider fiber cables. They are much more difficult to tap than copper cables.
Spark hazard – Oil and gas processing plants and mines are two places where sparking can be hazardous. Fiber cables do not emit sparks. Copper cables, on the other hand, are susceptible to spark hazards unless adequately protected.
Durability– Fiber cables are naturally more durable than copper, meaning they can withstand tougher environments and harsher weather conditions. When copper is the choice, it is important to choose the correct jacketing and shielding for protection (see below).
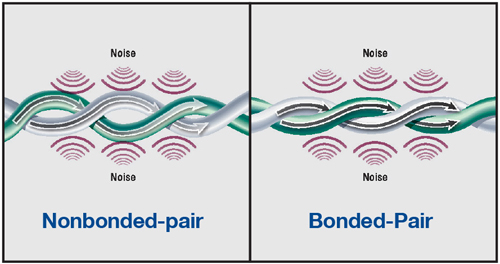
Noise immunity – When the cables are to be deployed in a location where there is significant electrical noise, special consideration is needed. Fiber cables are immune from electrical noise, whereas copper requires extra protection in the form of proper shielding and Bonded-Pair technology. Bonded-Pair technology ensures that the twisted pair of copper conductors inside a cable will not be distorted through twisting, bending or pulling of the cable itself. This provides for greater signal integrity in noisy or stressful environments.
One of the newest types of copper cable to be introduced to the market is 600-V, tray-rated Cat 5e cable, using Bonded-Pair technology, which is particularly designed to run in pre-existing cable trays throughout a factory. This type of cable is shielded against the high electromagnetic interference typically found in 600-V cable trays.
Choosing the right jacket and shielding
The characteristics of the conductors are only one piece of the puzzle. After choosing the right kind of conductor for your needs, the next step is to make sure your cable is protected. In industrial environments, cables can be subjected to many hazards, including extreme temperatures, moisture, UV rays, oil and corrosives. The type of jacket you choose will make a difference in how the cable performs. The table to the left lists some of the common environmental issues and the type of jacket required to counter them.
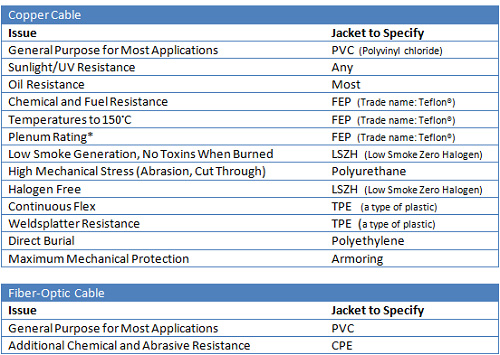
Cables are also in danger of damage through crushing or puncturing. You can protect your cable by running it through conduit, or you can use armored cables. Armored cables are easier to install and relocate than conduits, and there are a variety of armor options. If you foresee making changes to your physical layout, armored cables may be the better choice.
Cost
Copper cable has traditionally been less expensive. However, as with most budgetary decisions, the long-term effects of a choice have to be weighed against immediate costs. If you are on a tight budget and copper cable will fit your needs, then that will be your preferred solution. On the other hand, the growing demand for fiber cables is resulting in dropping prices, making cost less of an issue. It makes sense to review the requirements of the application and make decisions based on an in-depth evaluation of its true needs.
Specifying the right cables is one of the most important aspects of setting up a network in your industrial environment. The wrong cable can lead to equipment downtime, costing time and money. With upfront investigation into the broad range of industrial cable choices available today, you can easily identify the right cable and the proper protection. The right cable can provide years of trouble-free operation and deliver the lowest total cost of ownership.


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.